Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the leg. Understanding the DVT signs and symptoms is crucial because if the clot breaks loose, it can travel to the lungs and cause a life-threatening pulmonary embolism. Recognizing this condition early and knowing the DVT causes and risk factors can help you seek timely medical attention. This knowledge is your first line of defense against a potentially fatal event. If you ever suspect DVT, it’s vital to consult a medical professional, such as a vascular health specialist, immediately. Get a consultation with the best vascular disease specialists in Brooklyn.
DVT Signs and Symptoms: What to Look For
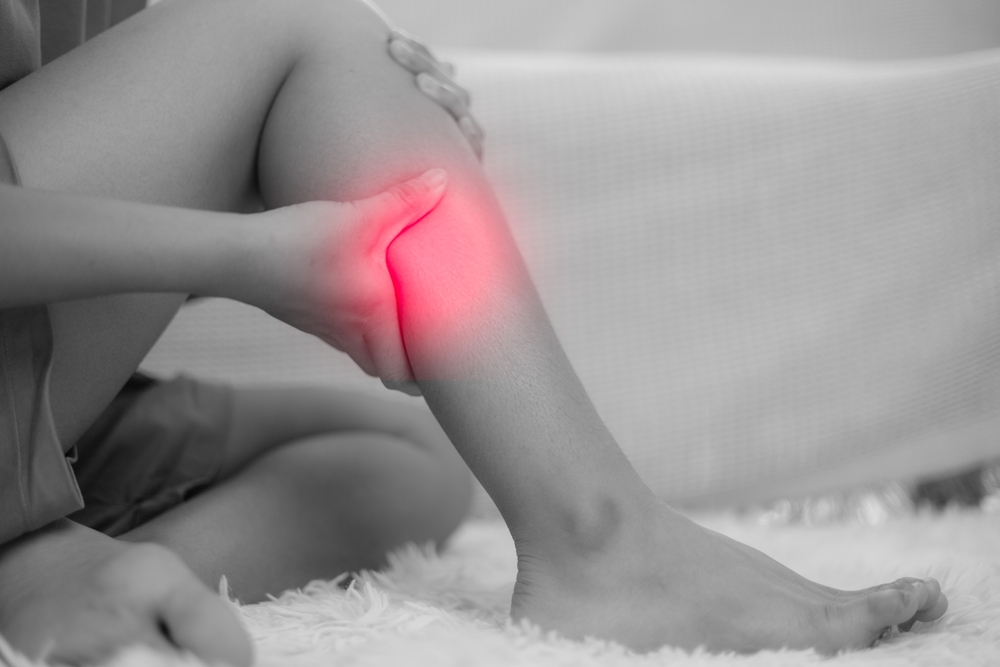
One of the most dangerous aspects of DVT is that it can occur with very few, if any, noticeable symptoms. However, when signs do appear, they typically affect one leg. It is essential to take these indicators seriously.
Key DVT signs and symptoms include:
- Swelling: Unexplained swelling in one leg, ankle, or foot is a classic sign.
- Pain or Tenderness: You might experience cramping or soreness in your calf, often described as a charley horse that won’t go away. The pain might only be present when standing or walking.
- Warmth: The skin on the affected area may feel warmer to the touch than the surrounding skin.
- Skin Discoloration: The skin over the affected vein might appear red or have a bluish tint.
It’s important to remember that about half of all people with DVT have no symptoms. Therefore, understanding your personal risk is just as important as recognizing the signs.
Understanding DVT Causes and Risk Factors
A DVT blood clot can form for several reasons, all of which relate to conditions that slow or change the flow of blood in the veins. The primary DVT causes, and risk factors can be grouped into a few main categories.
- Immobility or Limited Movement
When you are inactive for long periods, your calf muscles don’t contract, which helps blood circulate. Stagnant blood is more likely to clot.
- Prolonged Bed Rest: Hospitalization or paralysis can significantly increase your risk.
- Long-Distance Travel: Sitting for hours in a car, airplane, or train (“economy class syndrome”) can slow blood flow in the legs.
- A Sedentary Lifestyle: A lack of regular physical activity contributes to poor circulation.
- Injury or Surgery
Damage to a vein’s inner lining can trigger the body’s clotting response.
- Vein Injury: Trauma from a bone fracture, severe muscle injury, or a major accident can damage veins.
- Major Surgery: Operations, particularly those involving the hips, legs, or abdomen, are a significant risk factor. The recovery period often involves immobility, further increasing the risk.
- Medical and Genetic Conditions
Certain inherited or acquired conditions can make your blood more likely to clot.
- Inherited Clotting Disorders: Genetic conditions like Factor V Leiden can make your blood naturally “stickier.”
- Cancer: Some forms of cancer increase the number of clotting substances in your blood. Cancer treatments like chemotherapy can also raise the risk.
- Heart Failure: This condition makes it harder for the heart to pump blood effectively, leading to slower blood flow.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Conditions like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis are associated with a higher risk of DVT.
- Other Contributing Factors
- Age: Being over 60 increases your risk, though DVT can occur at any age.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts more pressure on the veins in your legs and pelvis.
- Pregnancy: The pressure of the uterus on the veins in the pelvis can slow blood return from the legs. The risk remains elevated for about six weeks after giving birth.
- Hormone-Based Medications: Birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy can increase your blood’s clotting ability.
- Smoking: Tobacco use affects blood circulation and the clotting process.
When to Seek Medical Attention
DVT is a medical emergency. If you experience any of the signs or symptoms, you should seek immediate medical care. If you experience chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or coughing up blood, call 911 immediately, as these could be signs of a pulmonary embolism.
For a proper diagnosis and management plan, it is best to consult with a vascular health specialist. They have the expertise to perform the necessary tests, such as a duplex ultrasound, to confirm the presence of a clot and prescribe the right treatment. For those in New York, a specialized vascular clinic in Brooklyn can provide expert diagnosis and ongoing care.
Take Action to Protect Your Health
Understanding the DVT signs and symptoms and knowing your own risk factors are powerful tools for prevention. If you have multiple risk factors, speak with your doctor about preventive measures, especially before surgery or long-distance travel. Should you notice any concerning symptoms, don’t wait. Contact a healthcare provider or visit a vascular clinic in Brooklyn for an expert evaluation. Prompt action can save your life. For any vascular problems, call us on + 1-718-367-2555. The Vascular Disease Specialists at Doral Health & Wellness consistently have outstanding patient satisfaction ratings. The professionals at Doral Health & Wellness Vascular Health Department Brooklyn can improve your health and quality of life because of their vast training and experience. New Yorkers can get the greatest medical and surgical vascular care at Doral Health & Wellness Brooklyn. If you need help, register your information and make direct contact with our doctors at https://yuz88hfiyh7.typeform.com/Doralintake or send an email to info@doralhw.org. Visit us at 1797 Pitkin Avenue, Brooklyn, NY 11212.