The term “flat feet” is widely known, but many people don’t fully understand what it means or that it can be a source of significant pain and discomfort. This guide on Flat Foot: Common Causes, Risk Factors, and Symptoms Explained aims to demystify the condition. While many people with flat feet experience no issues, for others, the lack of a proper arch can lead to a cascade of problems affecting the feet, ankles, knees, and even the back. Understanding the common flat foot causes, recognizing the key flat foot risk factors, and identifying the main flat foot symptoms are the first steps toward finding relief. Get a consultation with the best Podiatrists in Brooklyn.
What Are Flat Feet?
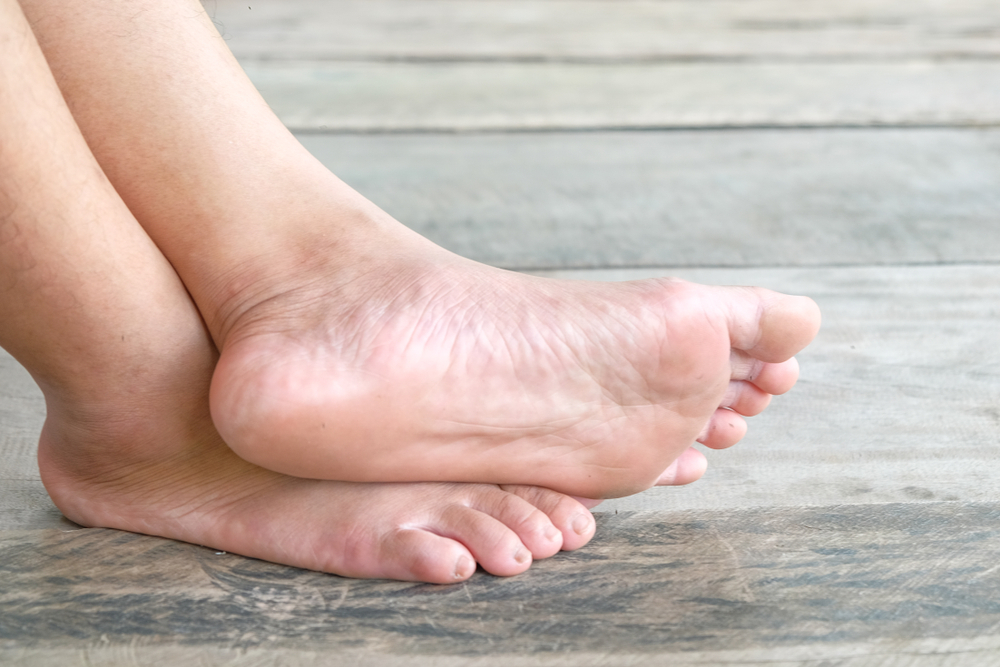
Flat feet, medically known as pes planus, are a condition where the arches on the inside of your feet are flattened, allowing the entire sole of your foot to touch the floor when you stand up. The arch provides a spring to your step and helps distribute body weight across your feet and legs. When the arch collapses, it can cause stress and misalignment throughout the body.
There are two main types:
- Flexible Flat Foot: This is the most common type. The arches are visible when the person is sitting, but they disappear upon standing. It typically begins in childhood and often does not cause pain.
- Rigid Flat Foot: In this type, the arches are not present whether the person is sitting or standing. It is less common and more likely to cause pain or discomfort.
Flat Foot Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what contributes to the development of flat feet can help in both prevention and management. The causes and risk factors often overlap.
Common Flat Foot Causes
- Genetics: This is one of the most significant factors. Many people simply inherit flat feet from their parents. If it runs in your family, you are more likely to have it.
- Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD): The posterior tibial tendon is the main support structure for the arch. If this tendon becomes injured, inflamed, or torn from overuse or injury, it can no longer support the arch, leading to an acquired flat foot in adults. This is one of the most common causes of adult-acquired flat feet.
- Injury: A traumatic injury to the foot or ankle, such as a fracture or dislocation, can damage the tendons and ligaments that support the arch, leading to its collapse.
- Childhood Development: While babies are born with flat feet, the arches typically develop throughout childhood. For some, these arches never fully form.
Major Flat Foot Risk Factors
- Obesity: Excess body weight puts immense pressure on the feet and can strain the posterior tibial tendon, contributing to the flattening of the arches over time.
- Aging: The natural aging process can weaken the posterior tibial tendon. Years of wear and tear can cause it to stretch and lose its ability to support the arch.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Diseases that affect the muscles and nerves, such as diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis, can increase the risk of developing flat feet. Diabetes, in particular, can cause nerve damage (neuropathy), which weakens the foot muscles.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause ligaments to become more lax. Combined with weight gain, this can lead to a temporary or sometimes permanent collapse of the arches.
Common Flat Foot Symptoms to Watch For
Many people with flat feet never experience any symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they can range from mild to severe. Pay attention to the following signs:
- Foot Pain: This is the most common complaint. Pain is often felt in the arch and heel area. It may worsen with activity.
- Leg and Back Pain: The lack of proper alignment in the feet can cause a chain reaction. This can lead to strain on the ankles, knees, hips, and lower back.
- Swelling: You might notice swelling along the inside of your ankle, which can be a sign of an inflamed posterior tibial tendon.
- Tired or Achy Feet: Your feet may feel easily fatigued, especially after long periods of standing or walking.
- Uneven Shoe Wear: Check the soles of your shoes. People with flat feet often show excessive wear on the inside edges.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you are experiencing persistent pain or any of the symptoms listed above, it is time to consult a specialist. A podiatrist is an expert in diagnosing and treating conditions of the foot and ankle. They can perform a thorough evaluation to determine the cause of your flat feet and recommend an appropriate treatment plan.
A visit to a podiatry clinic in Brooklyn will likely involve a physical examination of your feet, an analysis of how you walk (gait analysis), and potentially imaging tests like X-rays to assess the bone structure. A qualified podiatrist can offer a range of treatments, from custom orthotics to physical therapy, to alleviate your symptoms. For expert care, seeking a professional at a dedicated podiatry clinic in Brooklyn is your best course of action.
Don’t dismiss foot pain as a normal part of life. Understanding the causes, risks, and symptoms of flat feet can empower you to seek the right help and get back on your feet comfortably. At Doral Health & Wellness, we have Podiatrists with extensive education and expertise. Our address is 1797 Pitkin Avenue, New York, NY 11212. To make an appointment, please call + 1 718 367 2555, or register your information and make direct contact with us at https://yuz88hfiyh7.typeform.com/Doralintake or send an email to info@doralhw.org.