Receiving a dementia diagnosis is life-changing for both the individual and their family. When the diagnosis is vascular dementia, understanding the next steps is crucial. A clear path for vascular dementia diagnosis and management provides families with a roadmap for what lies ahead. Unlike other dementias, this condition is tied to cardiovascular health, which means the approach to vascular dementia management is unique. A timely and accurate vascular dementia diagnosis is the first step toward slowing the disease’s progression and maximizing quality of life through comprehensive dementia care. Visit the best Mental Health Clinic in Brooklyn at Doral Health & Wellness, or log on to www.doralhw.org.
The Process for Vascular Dementia Diagnosis
Diagnosing vascular dementia is a multi-step process designed to rule out other conditions and confirm that cognitive changes are due to vascular problems in the brain. There isn’t a single test for it; instead, specialists use a combination of assessments.
- Medical History and Symptom Review
The process begins with a thorough review of the person’s medical history. A doctor will ask about past health issues, particularly those related to heart and blood vessel health, such as:
- A history of stroke or mini-strokes (TIAs)
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Heart disease
The doctor will also want to know when the cognitive symptoms began and how they have progressed. In vascular dementia, symptoms often appear suddenly after a stroke or in a “step-wise” pattern of decline, which is a key clue.
- Neurological and Cognitive Testing
A specialist will conduct tests to assess memory, reasoning, judgment, and other thinking skills. These tests help identify the specific cognitive domains that are affected. This can involve simple questions and tasks in the office or more detailed neuropsychological testing, which provides a comprehensive profile of cognitive strengths and weaknesses.
- Brain Imaging
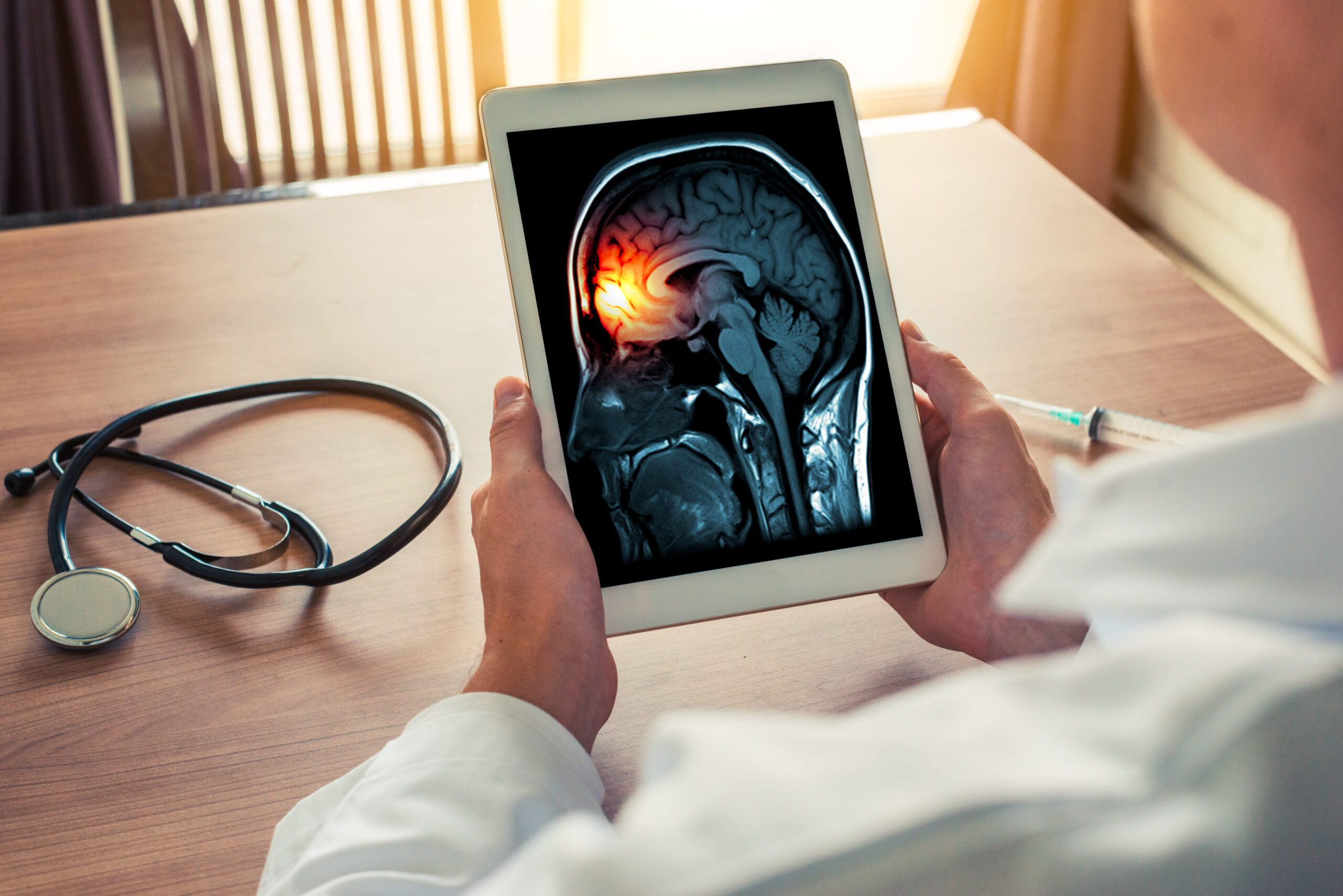
Brain scans are essential for a vascular dementia diagnosis. They allow doctors to see evidence of vascular damage in the brain.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This is the preferred method as it can show signs of recent strokes, mini-strokes, or damage to the brain’s small blood vessels (white matter lesions).
- CT (Computed Tomography): A CT scan can also reveal evidence of strokes and is often used in emergencies or if an MRI is not possible.
- Laboratory Tests
Blood tests are used to rule out other potential causes of cognitive symptoms, such as thyroid problems or vitamin deficiencies. They also help assess cardiovascular risk factors by checking cholesterol and blood sugar levels.
Effective Vascular Dementia Management Strategies
While there is no cure for vascular dementia, management focuses on two main goals: preventing further vascular damage and managing current symptoms to improve quality of life.
- Managing Cardiovascular Risk Factors
This is the cornerstone of vascular dementia management. By aggressively treating the underlying conditions that cause vascular damage, it’s possible to slow the progression of the disease. This includes:
- Controlling High Blood Pressure: Using medication and lifestyle changes to keep blood pressure within a healthy range.
- Managing Diabetes: Keeping blood sugar levels under control through diet, exercise, and medication.
- Lowering Cholesterol: Using statins or other medications to reduce high cholesterol.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption.
- Medications for Cognitive and Behavioral Symptoms
While no drugs are specifically approved to treat the cognitive symptoms of vascular dementia, some medications used for Alzheimer’s disease may be prescribed. More commonly, medications are used to manage related behavioral and psychological symptoms, such as depression, anxiety, or agitation.
- Therapies and Support
A holistic approach to dementia care is vital. Non-medical therapies can significantly improve daily functioning and well-being.
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: Therapists can teach strategies to help compensate for memory loss and other cognitive changes.
- Physical and Occupational Therapy: These can help with mobility, balance, and adapting daily tasks to make them safer and easier.
- Speech Therapy: This can help with communication difficulties that may arise.
Managing vascular dementia is a team effort. Building a strong support network of medical professionals is essential. A behavioral doctor is a key member of this team, as they specialize in managing the mood and behavioral changes that often accompany dementia.
For families navigating this journey, seeking support is not a sign of weakness but a crucial step toward sustainable care. A local mental health clinic in Brooklyn can provide access to valuable resources like caregiver support groups, counseling, and educational workshops. Consulting with a behavioral doctor can equip you with the tools to handle challenges effectively. A comprehensive mental health clinic in Brooklyn can be an invaluable partner, offering the community expert guidance needed for long-term dementia care.
With a clear diagnosis and a proactive management plan, individuals with vascular dementia can maintain a high quality of life, and their families can feel empowered to provide the best possible care. For further inquiries, call us on +1-718-367-2555 to get a consultation. Or log on to www.doralw.org. Visit us at 1797 Pitkin Avenue, Brooklyn, NY 11212. If you need help, register your information and make direct contact with us at https://yuz88hfiyh7.typeform.com/Doralintake.